Area councils in Abuja, Abuja administrative divisions, local government Abuja
Posted on 05/11/2024 3:00 PM | by NaijaHouses
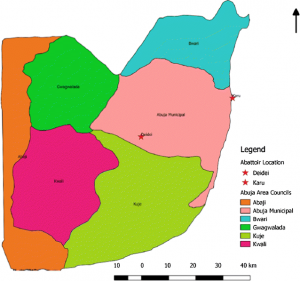
Area Councils in Abuja: Understanding the Heart of Nigeria’s Capital
Abuja, the capital city of Nigeria, is not only a political and administrative powerhouse but also a growing hub of culture and commerce. To effectively govern this expanding metropolis, Abuja is divided into six distinct area councils. Each council serves as a local government unit, managing essential services and ensuring that the city operates smoothly. This article explores each of the area councils in Abuja, shedding light on their unique characteristics, administrative functions, and the role they play in the capital’s development.
Introduction to Abuja’s Area Councils
In Abuja, the concept of area councils aligns with the local government structure seen throughout Nigeria. These councils operate under the Abuja Municipal Area Council (AMAC), but each one has its jurisdiction and responsibility for public services, urban planning, and community welfare. Understanding the area councils is essential for residents, business owners, and anyone looking to connect with the community or establish roots in Nigeria’s capital.
Overview of the Six Area Councils in Abuja
Abuja's six area councils include:
- Abuja Municipal Area Council (AMAC)
- Gwagwalada Area Council
- Kuje Area Council
- Bwari Area Council
- Abaji Area Council
- Kwali Area Council
These councils collectively support a diverse population and help in the organized expansion of the city. Each has its administrative offices and is led by a chairman elected by the residents.
Abuja Municipal Area Council (AMAC)
Key Facts about AMAC
Abuja Municipal Area Council (AMAC) is the most populous and economically dynamic of all the councils. It covers Abuja’s central areas, including the Federal Capital City (FCC) and surrounding districts like Garki, Maitama, Wuse, and Asokoro. AMAC is often the first point of contact for tourists and business travelers, as it includes the primary government buildings, embassies, and commercial districts.
Functions of AMAC
- Urban Planning: AMAC oversees urban planning and infrastructural development within the city center.
- Healthcare and Education: It manages several public health facilities and primary schools.
- Environmental Management: Waste management and sanitation fall under AMAC's purview.
AMAC also plays a significant role in Abuja’s social and cultural activities, with many citywide events held in its jurisdiction.
Gwagwalada Area Council
Location and Importance
Gwagwalada, located southwest of Abuja city center, is known for its residential neighborhoods and educational institutions, including the University of Abuja. Its strategic location and extensive road networks make it an essential area for commuters and residents.
Administrative Responsibilities
- Healthcare Services: The council operates several health centers, providing medical services to the community.
- Road Maintenance: Given the heavy commuter traffic, Gwagwalada’s road infrastructure requires frequent attention.
- Educational Support: Home to the University of Abuja, Gwagwalada contributes significantly to the city’s educational landscape.
Gwagwalada’s blend of residential, academic, and commercial areas makes it a lively part of Abuja’s urban tapestry.
Kuje Area Council
Overview of Kuje
Kuje is located south of the city center and is known for its semi-urban atmosphere. With a growing number of residential estates, Kuje is fast becoming an attractive suburb for families and professionals. It also has a mix of rural and urban settlements.
Key Responsibilities
- Agricultural Development: Kuje has a large agricultural sector, supporting farming communities within its boundaries.
- Basic Infrastructure: The council works to improve road networks and provide basic amenities to its residents.
- Community Welfare: Initiatives such as healthcare outreach and youth empowerment are prioritized here.
Kuje’s proximity to Nnamdi Azikiwe International Airport makes it a notable area for travelers and investors interested in suburban development.
Bwari Area Council
Unique Characteristics of Bwari
Bwari lies northwest of the central area and is known for its lush landscapes, traditional villages, and educational institutions, including the Nigerian Law School. This area council combines the serenity of rural life with growing urbanization, attracting residents looking for a more relaxed pace of life.
Administrative Scope
- Educational Services: Bwari’s prominence in education extends beyond the Nigerian Law School, as the council supports several secondary and primary schools.
- Rural Development: Many communities within Bwari are rural, so the council emphasizes rural development projects.
- Cultural Preservation: Bwari has a rich cultural heritage, and the council promotes local customs and festivals.
Bwari is a popular choice for students and families due to its tranquil environment and commitment to education and culture.
Abaji Area Council
Key Aspects of Abaji
Located at Abuja's southwestern tip, Abaji is the most distant council from the city center, giving it a more rural character. Abaji has a distinct identity rooted in traditional culture and agriculture, with many indigenous communities.
Core Responsibilities
- Agricultural Support: Abaji supports large-scale farming and agricultural development.
- Infrastructure Development: The council is working to improve roads, water supply, and healthcare access.
- Traditional Governance: Abaji respects traditional governance structures, incorporating them into local administration.
Abaji serves as a peaceful haven for those who prefer a countryside lifestyle within the Federal Capital Territory (FCT).
Kwali Area Council
About Kwali
Kwali, situated to the southwest of Abuja, is known for its pottery and traditional craftsmanship. This council has a strong artisan community and is respected for its dedication to preserving and promoting Nigerian cultural art.
Primary Roles
- Artisan Support: Kwali council promotes local artisans, particularly pottery makers, through events and market support.
- Basic Public Services: The council provides essential services, including healthcare, sanitation, and community development.
- Economic Development: Kwali seeks to attract tourism and investments, especially within its arts and crafts sectors.
Kwali has an enduring legacy in pottery, making it a cultural hub for locals and tourists who wish to experience Nigeria’s rich craft traditions.
Functions and Importance of Area Councils in Abuja
Each area council in Abuja plays a critical role in managing day-to-day governance, public welfare, and local services. Their functions include:
- Urban Planning and Zoning: Councils ensure that zoning regulations align with the Federal Capital Development Authority (FCDA) policies.
- Infrastructure Development: Roads, water supply, and sanitation services are managed locally.
- Education and Health Services: Area councils operate primary schools and health clinics, making these services accessible to residents.
How the Area Councils Contribute to Abuja’s Development
Area councils in Abuja serve as the bridge between the central government and local communities. They ensure that the FCT’s developmental agenda reaches all residents, providing equitable access to essential services. Their efforts in urban planning, rural development, and community engagement are vital to Abuja’s sustainable growth.
Challenges Faced by Area Councils in Abuja
Despite their importance, Abuja’s area councils face several challenges:
- Resource Constraints: Limited funding often restricts the scope of projects they can undertake.
- Population Growth: Rapid urbanization puts pressure on infrastructure and public services.
- Coordination with Central Authorities: Balancing local needs with central government directives can sometimes be challenging.
Addressing these challenges is essential to ensuring the area councils can meet the needs of Abuja’s residents.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of area councils in Abuja?
Area councils manage local governance issues, including infrastructure, healthcare, education, and public services.
How many area councils are there in Abuja?
Abuja has six area councils: Abuja Municipal, Gwagwalada, Kuje, Bwari, Abaji, and Kwali.
Which area council is closest to Abuja's central business district?
The Abuja Municipal Area Council (AMAC) is closest to the central business district and covers major urban areas like Maitama, Wuse, and Asokoro.
What is the largest area council in Abuja?
Abuja Municipal Area Council (AMAC) is the largest in terms of population and economic activity.
Are there traditional governance structures within Abuja’s area councils?
Yes, some councils, like Abaji, incorporate traditional governance into their administration.
How are the area councils funded?
Area councils receive funding from the federal government and may generate revenue from local taxes and levies.
Conclusion
The area councils in Abuja are fundamental to the capital's administrative structure, providing localized governance and community support across diverse regions. From the bustling heart of AMAC to the culturally rich council of Kwali, each area contributes uniquely to Abuja’s identity and growth. Through dedicated service, cultural preservation, and urban development, these councils help make Abuja a dynamic, inclusive, and thriving city. As the capital continues to evolve, the role of its area councils will remain crucial in shaping a sustainable and prosperous future for all residents.